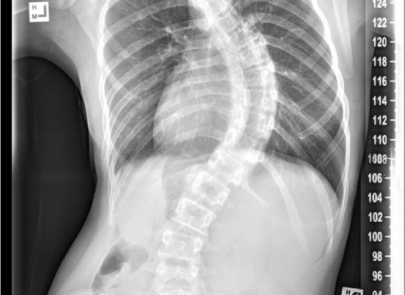
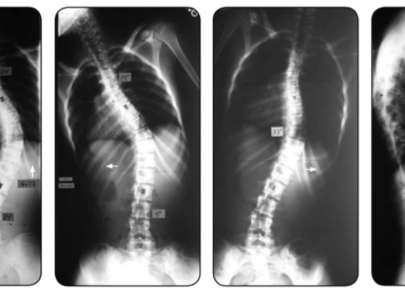
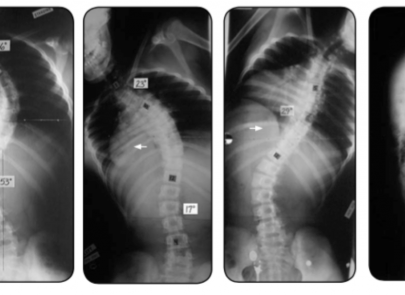
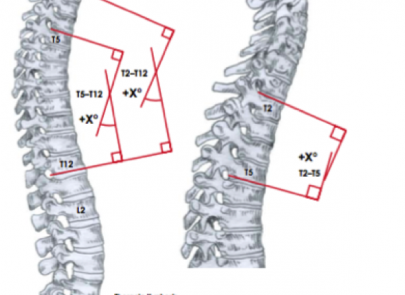
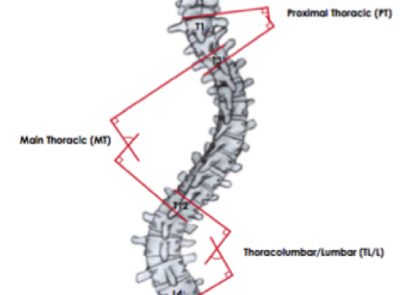
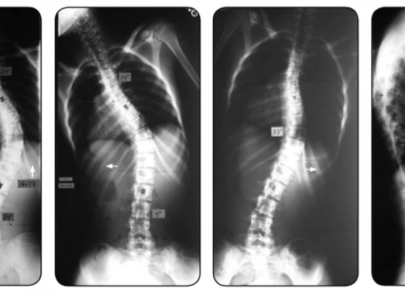
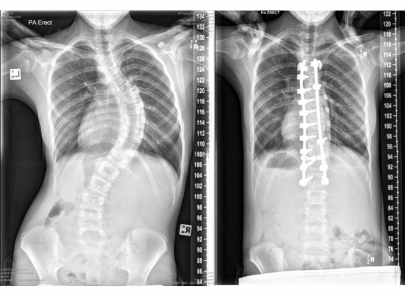
Scoliosis is a common condition that affects many children, adolescents, and can impact individuals right through into adulthood. Simply defined, scoliosis is a sideways curvature of the spine that measures greater than 10 degrees. It also includes an amount of spinal column rotation.
The most common diagnosis of scoliosis is Idiopathic Scoliosis – with “idiopathic” referring to the cause being unknown.
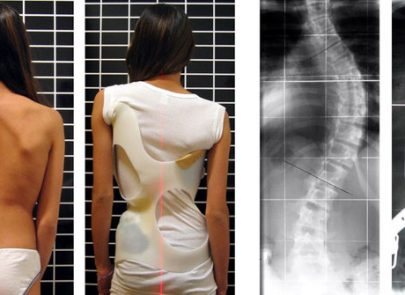
A spine with scoliosis curves will sometimes looking like a letter “C” or “S” rather than a looking like a line straight down the middle of the back.
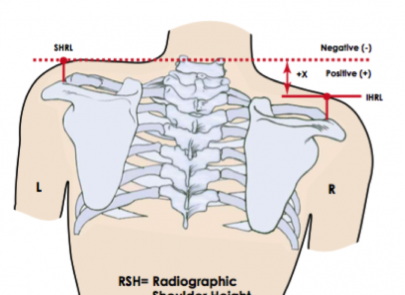
Patients usually suffer from a rotation of the spine which would make the waist or shoulders appear uneven.
- Infantile idiopathic scoliosis is the term used to describe scoliosis found in children from 0 to 3.
- Juvenile idiopathic scoliosis is the term used to describe scoliosis found in in children from 4 to 10.
- Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis is the term used to describe scoliosis found in adolescents from 11 to 18.
- Adult idiopathic scoliosis is found in patients over 18.